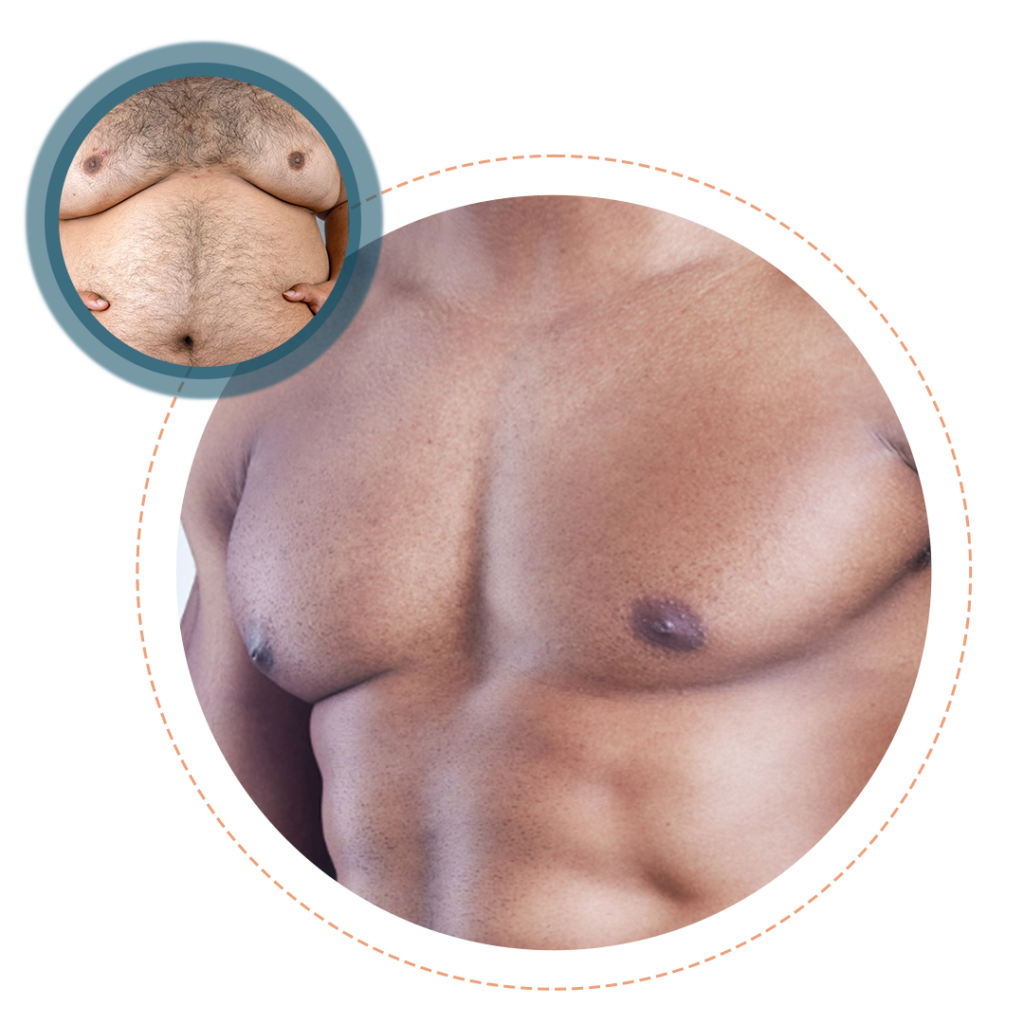
What is Gynecomastia?
Overview Gynecomastia treatment addresses the condition of enlarged breast tissue in males, which can be caused by hormonal imbalances, certain medications, or underlying health issues. The treatment aims to reduce the size of the breast tissue, providing a more typical male chest contour. Options include medication, lifestyle changes, and surgery, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Causes Gynecomastia is caused by an imbalance between estrogenic and testosterone hormones. Factors contributing to this imbalance include puberty, aging, use of certain medications (such as anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, and some antidepressants), chronic liver or kidney diseases, and conditions affecting the thyroid or pituitary glands.
Solutions The treatment of gynecomastia targets the underlying hormonal imbalance or medical condition. This can involve hormone therapy, medication adjustments, or surgical intervention to remove excess breast tissue. In cases where lifestyle factors are the cause, changes in diet, exercise, and weight management can help reduce the condition’s severity.
Types of Treatments
Medication-Based Treatment
Medications like tamoxifen or raloxifene can help reduce breast tissue size in men by addressing hormonal imbalances. These drugs are typically used in cases where gynecomastia is painful or persistent.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly reduce mild cases of gynecomastia. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding substances that can affect hormone levels, such as alcohol and drugs.

Surgical Treatment
Surgical options, such as liposuction or mastectomy, are considered for severe cases. Liposuction removes excess fat but not breast gland tissue, while mastectomy involves the removal of breast gland tissue, often through small incisions to minimize scarring.
Surgery Procedures and Recovery Time
Procedure Gynecomastia surgery typically starts with anaesthesia followed by liposuction and gland excision. Gland excision done by making small incision around the Areola .Depending on the extent of tissue removal required, the surgeon may perform liposuction, excision, or a combination of both. The procedure generally lasts about 1-2 hours, and the incisions are closed with sutures.
Recovery The recovery from gynecomastia surgery involves managing swelling, bruising, and discomfort with prescribed medications. Patients are advised to wear compression garments to support the healing tissues and minimize swelling. Light activities can usually be resumed within a few days, but strenuous activities should be avoided for 4-6 weeks. Full recovery and final results can take several months to become apparent.
Video About Treatment
FAQ
Gynecomastia treatment involves methods to reduce enlarged breast tissue in males, such as medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
The surgery typically takes about 1-2 hours, depending on the complexity and extent of tissue removal required.
The cost ranges from ₹50,000 to ₹1,50,000, depending on the surgeon’s experience and the facility.
Possible side effects include swelling, bruising, pain, and temporary numbness. Serious complications are rare but can include infection and scarring.
Initial recovery takes about 1-2 weeks, but full recovery can take several months. Patients should avoid strenuous activities for at least 4-6 weeks.
It is caused by an imbalance between estrogenic and testosterone, and factors include puberty, aging, medications, and certain medical conditions.
No. Gynecomatia once diagnosed it can be corrected only by surgery
Yes, it is generally safe when performed by a qualified surgeon. Risks are minimized with proper pre-operative and post-operative care.
Preparation includes medical evaluations, stopping certain medications, quitting smoking, and following the surgeon’s instructions.
Expect swelling and discomfort, manageable with medication. Wearing a compression garment and following care instructions will aid recovery.